skin disorder and diseases,
Skin Disorders and Diseases
Skin disorders and diseases can affect people of all ages and backgrounds, impacting not only physical health but also self-esteem and quality of life. Understanding these conditions, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options, is crucial for effectively managing them and maintaining healthy skin. This comprehensive guide will delve into various aspects of skin disorders, from common types to preventive measures and holistic approaches.
1. Introduction
Our skin, the body’s largest organ, serves as a protective barrier against external threats and regulates body temperature. However, it is susceptible to a range of disorders and diseases due to various factors such as genetics, environmental triggers, and lifestyle choices. By gaining insight into these conditions, individuals can take proactive steps to care for their skin and minimize the risk of developing or exacerbating skin problems.
2. Common Skin Disorders
Skin disorders encompass a wide range of conditions, each with its own set of symptoms and treatment approaches. Some of the most prevalent skin disorders include:
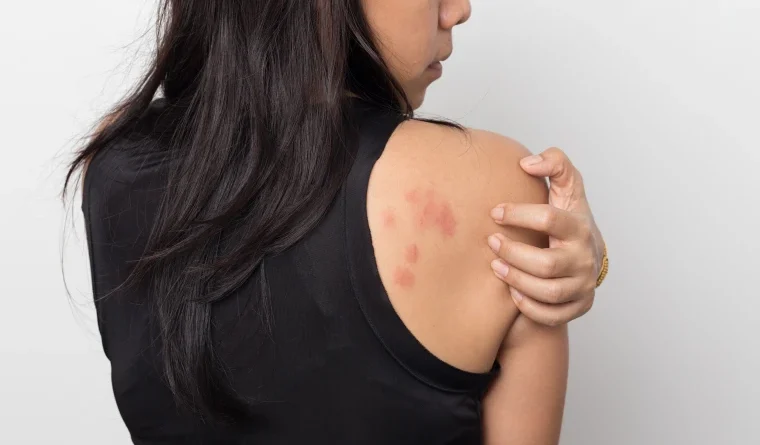
2.1 Acne skin diseases and disorders
Acne is a common skin condition characterized by the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads, often occurring during puberty due to hormonal changes. Excess oil production, bacteria, and inflammation contribute to its development.
2.2 Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed patches of skin. It is often triggered by environmental factors, allergens, or stress, and can vary in severity from mild to severe.
2.3 Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the rapid proliferation of skin cells, leading to thick, red, and scaly patches. It can cause discomfort and affect quality of life, with flare-ups triggered by stress, infections, or certain medications.
2.4 Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, flushing, and visible blood vessels. It may also lead to the formation of papules and pustules, often mistaken for acne.
3. Causes and Symptoms
Understanding the underlying causes and symptoms of skin disorders is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. While the exact cause may vary depending on the condition, common factors include:
3.1 Genetic Predisposition
Many skin disorders have a genetic component, meaning they tend to run in families. Individuals with a family history of eczema, psoriasis, or acne may have a higher risk of developing these conditions themselves.
3.2 Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors such as pollution, UV radiation, and harsh weather conditions can exacerbate existing skin conditions or trigger flare-ups. Protecting the skin from these triggers is crucial for maintaining its health and integrity.
3.3 Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can influence the development of skin disorders such as acne and eczema. Balancing hormone levels through medication or lifestyle adjustments may help manage these conditions.
4. Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing skin disorders often involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and sometimes, additional tests such as skin biopsies or allergy testing. Once diagnosed, treatment options may include:
4.1 Topical Medications
Topical medications such as corticosteroids, retinoids, and antimicrobials are commonly prescribed to alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation associated with skin disorders.
4.2 Oral Medications
In severe cases, oral medications such as antibiotics, immunosuppressants, or oral retinoids may be prescribed to control symptoms and prevent complications.
4.3 Phototherapy
Phototherapy, also known as light therapy, involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light under controlled conditions to reduce inflammation and promote healing in conditions such as psoriasis and eczema.
5. Lifestyle Factors
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can play a significant role in managing and preventing skin disorders. Factors such as diet, hygiene practices, and stress management can impact skin health.
5.1 Diet
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can support overall skin health and reduce inflammation associated with skin disorders. Avoiding trigger foods such as dairy, processed foods, and sugar may also help prevent flare-ups.
5.2 Hygiene Practices
Practicing good hygiene habits such as regular bathing, gentle cleansing, and moisturizing can help prevent infections and soothe irritated skin. However, excessive washing or harsh scrubbing can strip the skin of its natural oils and exacerbate certain conditions.
6. Skincare Tips
Effective skincare plays a crucial role in managing and preventing skin disorders. Adopting a consistent skincare routine tailored to individual skin types and concerns can help maintain skin health and reduce the risk of flare-ups.
6.1 Cleansing
Choose a gentle cleanser suitable for your skin type and use it twice daily to remove dirt, oil, and impurities without stripping the skin’s natural moisture barrier.
6.2 Moisturizing
Apply a moisturizer formulated for your skin type immediately after cleansing to hydrate and protect the skin. Look for non-comedogenic formulas to prevent clogged pores and breakouts.
7. Dietary Considerations
The foods we consume can significantly impact our skin health, either positively or negatively. Making dietary adjustments based on individual sensitivities and nutritional needs can complement medical treatment and promote skin healing.